If you woke up this morning to the news that a 3.8 magnitude earthquake struck near Melbourne, you might be wondering how that happened. We’ve long been taught in school that Australia doesn’t sit on a tectonic plate, so it’s incredibly unlikely that we will experience intense earthquakes – if any at all.
The 3.8 magnitude quake that struck Sunbury, west of Melbourne, which was felt as far south as Hobart, has probably left you wondering about Australia’s history of earthquakes and how they are different here from other regions.
It might come as a shock to you, but on average, Australia actually experiences around 100 earthquakes of magnitude 3 or more every year, according to Geoscience Australia. Earthquakes above magnitude 5.0 come every one-to-two years, and 6.0 or more every ten or so years.
So, let’s investigate Australia’s history of earthquakes and how they occur.
What is an earthquake?
If you need a refresher, Geoscience Australia describes an earthquake as the vibrations caused by rocks breaking from stress under the earth’s surface.
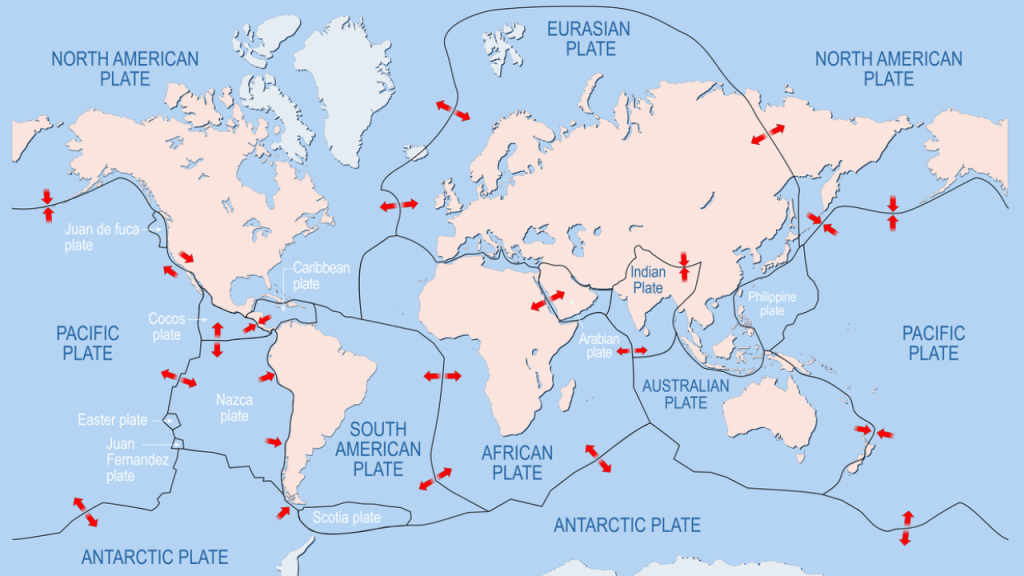
The earth is broken into fractures called tectonic plates, with fault lines between them. Earthquakes occur when there is sudden movement along these faults as a result of stored-up energy and long-term buildup of stress. When these movements occur, it ripples through the earth and causes the ground surface to shake.
You can read about the science of it all in more depth here.
The magnitude of earthquakes was originally measured on something called the Richter scale but is now calculated from seismic movement. This is a more accurate way of measuring earthquakes as it is proportional to the fault area multiplied by the average displacement on the fault, according to Geoscience Australia.
A magnitude 6.0 earthquake will release around 30 times more energy than a magnitude 5.0 earthquake, and so on. According to Geoscience Australia, a magnitude 8.6 earthquake releases energy equivalent to around 10,000 atomic bombs. For reference, the Boxing Day Indian Ocean tsunami was triggered by a magnitude 9.1 earthquake.
Obviously, the 3.8 earthquake recorded in Victoria is far less severe, but Australia has experienced some large earthquakes before.
Does Australia get earthquakes?
If you’ve read the news recently, you’d already know the answer to this question. Yes, Australia does get earthquakes. But they are a little different from other ones.
Turns out the Australian plate is actually the fastest moving continental land mass on Earth, colliding with the Pacific plate to the north and east, and also into the Eurasian Plate on the northwest. According to Geoscience Australia, we’re actually moving northeast around 7 cm per year.
As a result, this collision is causing stress within the Australian continent. This stress is, at times, suddenly released, causing earthquakes on Australia’s mainland.
But how big have Australia’s earthquakes been?
How many have we had?

Adam Pascale, chief scientist at the Seismology Research Centre, told the ABC that Victoria’s 3.8 earthquake may have been the largest in over 100 years within the Melbourne metro area.
You might recall that back in 2021, there was a magnitude 5.9 earthquake in Melbourne. However, the epicentre was about 130 km east, in Woods Point.
Nationally speaking, the largest recorded earthquake occurred back in 1988 in Tennant Creek, Northern Territory. That earthquake had a magnitude of around 6.6, which is pretty big, but because it was in a remote area, the only damage was to a gas pipeline.
The interesting thing about Tennant Creek is that the earthquake formed part of a series of shocks that reached a 6 or more magnitude.
The second-largest earthquake in Australia was recorded in 1968 in Meckering, Western Australia, where a 6.5 earthquake (originally recorded as 6.9) caused damage to buildings and was felt over most of southern Western Australia. According to Geoscience Australia, both of these earthquakes are two of the 11 that have produced surface ruptures.
Here are the biggest earthquakes recorded in Australia:
Data here is via the Australian Government’s Geoscience website.
- Tennant Creek, NT – 6.6 magnitude, 1988
- Meckering, WA – 6.5 magnitude, 1968
- Simpson Desert, NT – 6.4 magnitude, 1941
- Tennant Creek, NT – 6.3 magnitude, 1988
- Meeberrie, WA – 6.3 magnitude, 1941
- Collier Bay, WA – 6.2 magnitude, 1997
- Tennant Creek, NT – 6.2 magnitude, 1988
- Cadoux, WA – 6.1 magnitude, 1979
- Petermann Ranges, NT – 6.1 magnitude, 2016
- West of Lake Mackay, WA – 6.0 magnitude, 1970
As you can see, a majority of the big earthquake we’ve had in Australia have occurred in the western and northern parts of the country. Interestingly, only one earthquake in recent times (2016) has measured over 6.0 magnitude.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.