News feeds like Facebook’s shape how you see the world. Algorithms behind those sites determine what news is important enough for you to see. Their goal is to improve the relevance of the stories you read, but they have a nasty side effect: They control the flow of information, and you wind up in an echo chamber where you only hear ideas you agree with.
Illustration by Angelica Alzona.
On the surface, the idea of suggesting stories that are relevant to you makes sense. Google Now suggests articles they think you’ll like based on your search history. You can even prevent this feature from showing you stories about topics or from news sources you don’t like. After all, why would you want Google recommend garbage from sites you hate? However, the more you hear the same perspectives from the same sources, the more it reinforces your ideas without ever challenging them. It’s understandable if you don’t want to see articles about underwater basket weaving if you’re not into it, but when it comes to important topics, only getting news from one outlet colours your perceptions and even leads to a tribal mentality where we vilify anyone outside the group.
Algorithmic Feeds Encourage Bias, Even If They Don’t Mean To
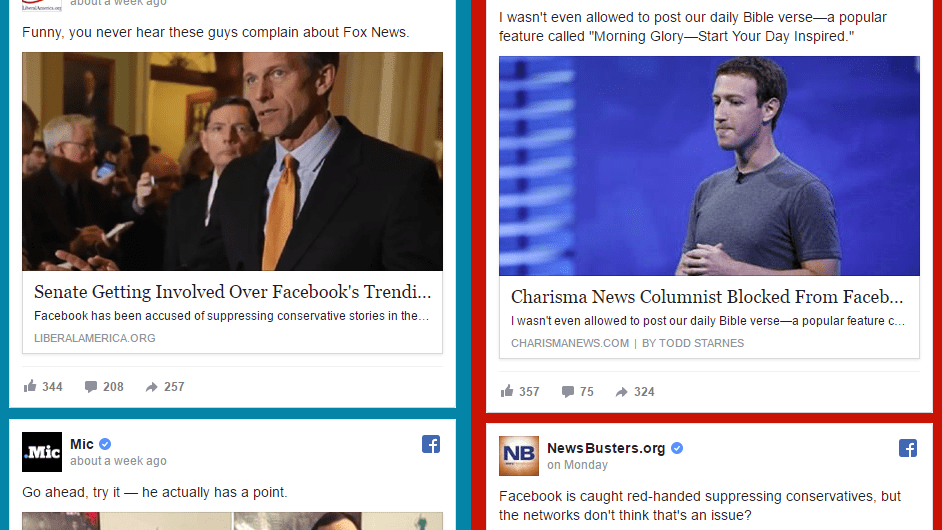
Facebook is the biggest publisher in the world. It’s the primary way most people hear and read the news. That also gives the social network a lot of influence over your perceptions. Earlier this year, we showed you how to find out what you’re interested in, which can include how you lean politically. As an interactive tool from the Wall Street Journal revealed, the version of a story you hear depends heavily on how you lean. If you read left-wing news sources (or even just have predominantly left-wing friends), Facebook will show you more left-leaning news. The same thing happens for conservatives and even the most fringe members of the political spectrum. In short, this algorithmically-enforced confirmation bias means the more you read information you agree with, the more Facebook will show you even more information you agree with.
Of course, the system works that way because we don’t like the idea of big companies deciding what we see for us. Earlier this year, Gizmodo revealed that Facebook routinely suppressed conservative news in its trending news module (which is separate from its News Feed). This led to the US Senate launching an investigation into the social media giant’s possible bias, after which Facebook removed all human curators from its news module. It even stopped summarising news stories. Now, trending news topics are designated simply by the subject of their story. If, for example, you want to know why John Oliver is in the news, you’ll have to click through to find out from a news source. You can’t get it from Facebook itself.
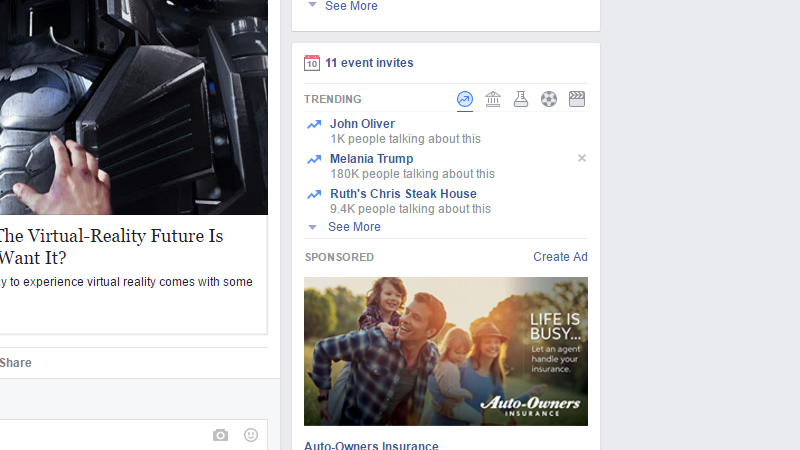
Facebook doesn’t even want to risk possible “bias” by including a whole headline.
Facebook isn’t alone. Google does this too. If you scroll down in Google Now on your smartphone, you’ll see recommendations for articles to read. These are chosen based on the topics you search for, which articles you choose to read and which news sources you frequent. In other words, Google also wants to give you more of what you’re already looking for.
While it’s handy, it’s certainly privy to bias — especially your own. Even worse, Google doesn’t care about the quality of the articles it shows you as long as they’re on topic. For example, Google knows I’m looking forward to the new season of Rick and Morty, so it routinely suggests any article that might have information about the potential release date for season three. Most of these articles are rehashes of completely crap rumours and hoaxes that have been debunked months ago, but that doesn’t matter. It says “Rick and Morty”, so I get the recommendations. This also happens when I read political news. If I click on one story about a particular politician, Google will recommend the most popular stories about that person, regardless of whether or not those stories are well-researched or even coherent. As long as I’ve “shown interest” Google thinks I should read about it.
Unfortunately, just showing you the articles that an algorithm thinks you want to see is a bit like only feeding you food that you find the tastiest. If a computer decided that you responded most positively to ice cream, you might never eat anything else again, but it won’t make you healthy. Likewise, Facebook and Google have a vested interest in showing you the stories you interact with the most. At best, those companies can try to avoid passing along obviously fake news, but it’s impossible to avoid encouraging your own subtle biases when the system rewards you with more things you like.
What You Can Do to Fight the Bias and Inform Yourself
Feedly lets you see which stories are popular (denoted by the orange highlighted numbers) without pushing down other stories.
Tailoring your news feeds to your interests isn’t necessarily bad. There’s no reason to read garbage sites that indulge in conspiracy theories, shamelessly lie or sling low-brow insults for a cheap laugh (unless you’re into that sort of thing). However, you can still do a few things to avoid creating your own echo chamber:
- Use news apps that don’t pick content for you. Algorithmic timelines are fine if you want to just get the gist of what’s going on today without diving too deep. If you want a wider viewpoint, subscribe to sites via a service like Feedly or use Twitter‘s chronological timeline. You can even keep using Facebook by sorting by Most Recent. Google News also collects related stories around a single topic in one place so you can see every viewpoint, rather than just being shown the one that lines up most with your views.
- Follow different news outlets with a variety of perspectives. The best way to get a wider understanding of your world is to read stories from many different viewpoints. Even if a news outlet tries its hardest not to be biased, others might catch something they miss or offer a perspective no one else thought of. When you fill up your feeds with the sources you want to read from, try to expand your list to include places that challenge you or propose ideas that you’re not familiar with. Challenging your own ideas is a powerful way to refine them.
- Pause before you jump on a story to consider your own biases. When you encounter a story about something crazy happening, pause for a moment and ask yourself, “Is this true?” Don’t share it just because it sounds true. Take a few minutes to do a little research and verify a story before you believe it. Discerning the truth on the internet is a lifelong skill and no one can ever expect to get it right all the time, but taking a few minutes to pause before you share or engage something can go a long way towards curbing misinformation online.
When a tech company decides to use algorithms to adjust the world to suit your viewpoints, it distorts your reality. That doesn’t mean all algorithms are bad, but we do need to be honest with ourselves about how our perception of world events are coloured by the news we see and read . If you want to avoid being a victim of the almighty algorithm, take your research into your own hands. Or, at the very least, accept that you’re only getting the part of the story that Google or Facebook thinks you’ll like the most.

Comments
2 responses to “How Sites Like Google And Facebook Put You In Political Echo Chambers”
I think that’s the saddest thing I’ve read this week.
Most Australians primarily get their news from News Limited publications, which is far worse.
Our future dystopian world is full of people who think he saved the world because he gave us all free web services with the extra bonus of keeping right up to date with current-ish world events. This is yet another reason Zuck should be banned from giving so-called “Free Internet” to the poor.