Avoiding needed medical care is generally a bad idea, reserved for people who are either lazy, scared or trying to save money. But too much medical care has its own risks. It can be smart to avoid certain tests or treatments and opt for second opinions instead of more visits, and a good provider can help you make that decision thoughtfully.
Illustration by Sam Woolley.
We’re not saying that you should ever turn down necessary care. When considering the cost of ambulance rides, sometimes people conclude that it is better not to call for help in an emergency. That’s not true, of course: It’s better to be alive and dealing with hospital bills than debt-free but dead. But in a lot of non-emergency situations, there is room for you — and your doctor — to rethink how much care you actually need.
One good place to start is at the Choosing Wisely website from the American Board of Internal Medicine. The board’s foundation asked medical associations to name the top five things in each field that patients and providers should reconsider. They have massaged those recommendations into fact sheets for patients, but you can also snoop on the ones intended for clinicians if you don’t mind wading through some medical lingo. Let’s look at some of the take-home messages.
Tests Have Risks and Benefits
You might think of a medical test as asking a simple question. Questions don’t sound harmful, so we (and doctors!) often like the idea of doing a test and finding out what’s wrong. But no test is perfect, and there are consequences to a test being wrong.
Take mammograms, for example. In the US, there are four different sets of guidelines about when you should start getting them, whether you should ever stop and how often they should be performed. Each represents a slightly different judgement call on how to balance the risks and the benefits of this arguably overhyped test.
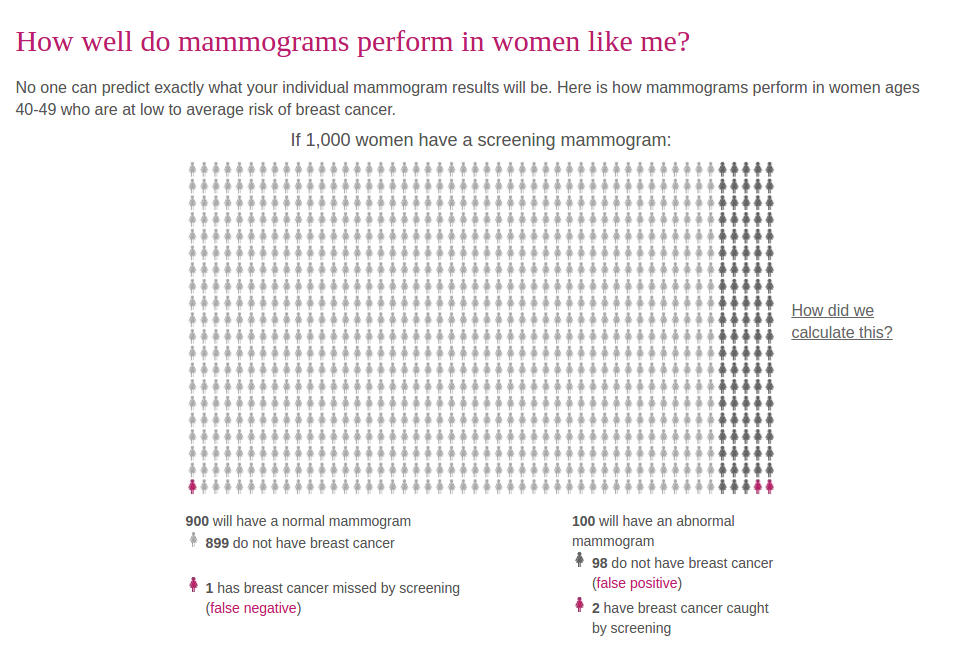
Take a look at this graphic representing the results of a mammogram for 1000 women at low to average risk of cancer. For every two cases of cancer the test detects, it misses one and flags another 98 women for additional testing. That means extra days or weeks of worrying whether you have cancer, A few of those women may end up getting surgery, radiation or chemo for a cancer they didn’t actually have. Some women with low cancer risks are more likely to be harmed than helped by mammograms. That doesn’t mean the test is useless, but it is a judgement call: Yours as well as your doctor’s.
Here are some more tests that, according to the Choosing Wisely recommendations, are worth questioning. Your doctor should be on board with the most recent guidelines, but sometimes old habits die hard.
- Annual pap tests to screen for cervical cancer. These used to be recommended annually, but cervical cancer develops so slowly, and the immune system so often takes care of it by itself, that annual tests are overkill. In Australia, the Cancer Council recommends a pap smear every two years. (In the US it’s recommended that most women should get tested every three to five years.)
- Blood tests for Vitamin D. These only make sense for people with certain diseases or risk factors. Vitamin D tests aren’t usually helpful for healthy people.
- PSA tests for prostate cancer screening. Blood tests can look for prostate-specific antigen (PSA) but there are far more false positives than useful results.
- Whole-body scans for cancer. They involve a lot of radiation, and often detect things that wouldn’t have been a problem. These incidental findings then require more observation over the years — which means more scans. Benefits only sometimes outweigh the risks.
- Blood tests for miscarriage risk. Most usually aren’t helpful and can lead to unnecessary treatment.
- Daily blood tests if you’re in the hospital. These are often ordered as a matter of routine, but it’s OK to ask if they’re really necessary. Sometimes they aren’t.
- Emergency room CT scans for minor head injuries. A CT scan can’t tell if you have a concussion, but it might be a good idea for a major injury where there might be bleeding in the brain. CTs are not only unhelpful, they’re also expensive and expose you (or your child) to radiation.
Many other tests, including cholesterol tests, osteoporosis tests and colon cancer tests, make sense for people at certain ages or with certain risk factors, but they’re not for everybody. See a rundown of useful tests and their age ranges on this fact sheet about checkups.
Treatments Have Risks and Costs, Too
Treatments also deserve scrutiny. Take antibiotics, for example. Once thought to be a low-risk treatment, we now recognise that side effects include wiping out our good bacteria, which can lead to yeast infections and sometimes severe diarrhoea. Too much antibiotic use also encourages antibiotic-resistant germs, like super-gonorrhoea and MRSA.
Not surprisingly, a lot of the Choosing Wisely guides are all about ways of avoiding antibiotics. But there are other treatments, too, that are worth questioning. Remember that every treatment has a cost, so even those that are harmless may still be a waste of time and money.
- Cancer treatment for somebody nearing the end of their life. Stopping treatment is a tough decision, but the chance that treatment might slightly extend a person’s life may not outweigh the fact that many of those extra days will be spent in chemo hell. It’s a discussion worth having. And even for patients with a good prognosis, sometimes a less-is-more approach (for example, with some types of radiation therapy) gives better outcomes.
- Surgery for plantar fasciitis. Non-surgical approaches often work better, and the surgery carries risks of permanent damage.
- Sleep studies for insomnia (but not sleep apnea) It’s usually possible to diagnose and treat insomnia without one. Sleep studies do help to diagnose sleep apnea.
- Too-easy physical therapy, which is often prescribed for older people out of a fear they will hurt themselves. But if exercises aren’t challenging, they aren’t helping.
- Urinary catheters increase the risk of a urinary tract infection, so they should only be used when necessary.
- Replacing mercury-containing fillings with non-mercury versions might sound like a good idea, but the replacement actually releases more mercury than leaving them in place. Most of the time, it’s best to leave them alone.
Sometimes one of these treatments or procedures will turn out to be a good idea for your particular situation, but it’s worth asking your doctor why she’s ordering it and whether other options might be better.
What Questions to Ask
For tests, it’s important to ask what decision will be based on the result. Just because a test is routine, or because you or your doctor is curious about the result, doesn’t mean the test is useful. For example, there are prenatal tests that can tell you whether your fetus seems to have a genetic abnormality. Since you could end up with a false positive or a false negative result, it’s worth asking yourself: Would you do anything differently (such as terminate the pregnancy) on the basis of those results? If not, it’s OK to say you would rather not have the test at all.
Medical professionals are all familiar with the idea of informed consent — where you, the patient, are entitled to know the risks and benefits of a test or treatment before you agree to it. No doctor will think you are weird if you ask:
- What are the risks of this test or treatment?
- What are the benefits?
- How likely is this treatment to work (or how likely is this test to give a correct result)?
- What else could we try instead?
You’re not being a bossy patient if you ask these questions, and you shouldn’t feel bad about asking them. And don’t forget to ask even if you’re the one who suggests the test or treatment. For example, if you hear about a really awesome-sounding medication and ask your doctor about it, don’t just say “Hey doc, can I have this?” but also ask about its risks and alternatives. Same idea if there’s a test you’ve heard everyone should get.
“There’s ample evidence that a significant percentage of elective care is given to patients who would have chosen to avoid it, had they better understood their choices and the tradeoffs involved,” three experts write at the Health Affairs blog. Learning about those choices and tradeoffs helps you to be a smarter, and perhaps a healthier, patient.
Comments