I’ll confess up front: I have terrible posture. It’s been bad since at least high school. It’s one of those things I keep in the back of my mind as something I know I should do but never get around to, like eating more vegetables and sending more postcards.
This post originally appeared on Buffer
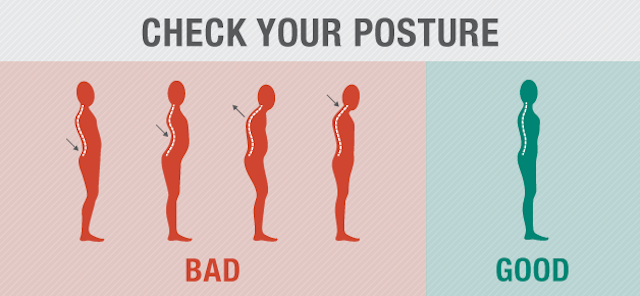
The way we stand, sit and walk, actually has more longer reaching implications on our mood and happiness than we thought. The latest studies reveal it:
Shaking Your Head Will Affect Your Opinion
Body language is closely related to posture — the way we move our bodies affects how others see us as well as our own moods and habits. In terms of scientific research, the two overlap quite a bit. This isn’t too surprising, but how our posture and body language affect our thoughts is.
For instance, a study at Ohio State University in 2003 found that our opinions can be subconsciously influenced by our physical behaviour. Here are two fascinating examples:
- When participants in the study nodded in agreements or shook their heads to signal disagreement, these actions affected their opinions without them realising.
- The same study also showed that when participants hugged themselves, they were sometimes able to reduce their physical pain.
Dutch behavioural scientist Erik Peper has done extensive research into this area, as well. He regularly makes participants in his classes stand up and stretch, for similar reasons why exercise has been linked to happiness, like here:
Here are three fascinating things that happened once our posture changes:
- For example, when we sit up straight, we are more likely to remember positive memories or think of something positive in general, according to this experiment.
- Another insight was that if we skip during breaks, we can significantly increase our energy levels. A slow, slumped walk on the other hand, can do the exact opposite and drain us of our energy.
- The study also found that those who were most affected by depression before the study found their energy drained more than others.
So Erik Peper is convinced (and I am, too) that we should keep a careful eye on our posture and body language — lest it bring us down without us realising.
Posture Changes Our Hormones
When we talk more broadly of body language, as opposed to good posture, we can actually see the affects it has on relationships right throughout the animal kingdom. In particular, body language is used to express power, through expansive postures (i.e. spreading out your limbs and opening up your body) and large body size (or the simple perception of large body size).
You might know about Amy Cuddy’s famous Ted Talk and her incredible insights on how posture changes our hormone levels. Well, some even more recent studies took this even further. A study by researchers from Columbia and Harvard Universities showed that body language symbolising power can actually affect our decision-making, subconsciously. The researchers measured the appetite for risk of participants in either expansive, powerful poses or constricted poses (occupying minimal space, keeping limbs close to the body). Those in the powerful poses not only felt more powerful and in control, but were 45% more likely to take a risky bet.
Plus, the study used saliva samples to prove that expansive postures actually altered the participants’ hormone levels — decreasing cortisol (C) and increasing testosterone (T):
This neuroendocrine profile of High T and Low C has been consistently linked to such outcomes as disease resistance and leadership abilities.
So clearly, our posture has more to do with our minds we might have thought. And in fact, it seems like our bodies come first — when we alter our posture and body language, it subconsciously influences our thinking and decision-making.
There’s No “One Best” Posture
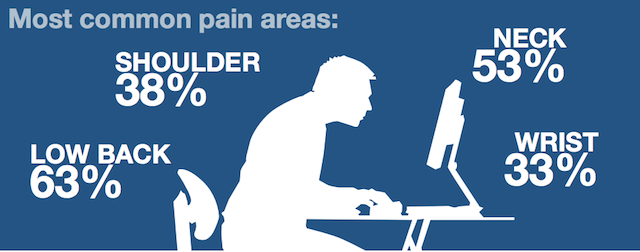
So if you want to take advantage of these proven benefits to live a healthier and happier life, where should you start? We know that there is a large amount of different areas that can be painful when we have bad posture. Here’s just a short list of them:
Unfortunately there’s not a whole lot of research into how exactly to adopt good posture — a lot of what we know tends to come from being told to “sit up straight” as children. A study in 1999, however, found that sitting at an angle of 110-130 degrees is optimal for spine comfort, and another in 2007showed that leaning back at 135 degrees is ideal for preventing back strain.
Not only is a position like this difficult to measure and maintain (do you know precisely what angle you’re sitting at right now?), not everyone agrees. The team at LUMOback have created a posture sensor that you can wear around your waist during the day to help you develop better posture. The device watches for slouching and shifting to the side, and vibrates to remind you to sit up straight.
The team, which includes a doctor and a data scientist (as well as a medical advisor), doesn’t advise the leaning-back position for your workday. Instead, they maintain firstly that “the best posture is always the next posture,” or in other words, always keep moving:
We know that many of us have jobs that do require us to spend time working at desks, so knowing how to sit and stand with good posture is certainly important and beneficial to one’s health and well-being. That said, the human body was built to move, not spend 8 hours at a computer.
While many of the apps and devices designed to track our daily activity focus on workouts and regular exercise routines, LUMOback is more focused on small, regular bursts of movement:
Walking around helps your body to reset itself into healthy posture, so make a point to get up from your desk at least twice an hour.
When it actually comes to posture, the LUMOback team recommends a neutral pelvic postion — i.e. sitting up straight. They promote this posture particularly for times when we’re sedentary for long periods, like sitting at our desks all day:
When you maintain a neutral pelvic position with a straight and upright back, the vertebrae in your back are nicely aligned. This takes a lot of pressure off of your spine and back muscles, which can reduce back pain.
Here’s an image from the study that promotes leaning back at 135º:
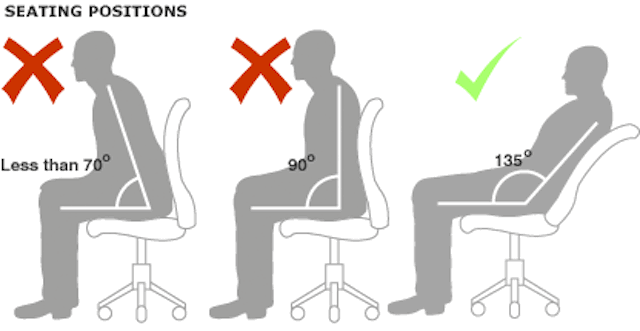
As the LUMOback team points out, while this is beneficial for your lower back (if you manage to keep it straight), your upper back and neck will suffer if you try to maintain this position while working.
In an office setting, you’re likely to have to crane your neck to see your computer screen and strain your upper back and shoulders to reach a keyboard. Thus, any potential lower back benefits of a reclined position are outweighed by the negative impacts on your upper back and neck.
For now, I’m going to give sitting up straight a go. If nothing else, at least I know it will probably put me in a good mood!
The Science of Posture [Buffer]
Belle Beth Cooper is a content crafter at Buffer and co-founder of Hello Code. She writes about social media, startups, lifehacking and science.

Comments
6 responses to “The Science Behind Posture And How It Affects Your Brain”
While that 135 degree seating position may be great in an aeroplane, it wont work at the office, or anywhere else for that matter.
Hence the need for standing desks wherever appropriate.
The LUMOback looks really interesting, and I know I have poor posture (from years of sitting in front of a computer with bad eyesight). The downside?
No Android support (yet). This is my biggest frustration, as it took Rockstar a month and a half to get an Android version of the iFruit app going. If you build your app right, cross-platform support comes easier.
Still, I’ll keep my eyes on this. Looks good.
I can’t read this article because of the two bars on the left hand side of the page that are blocking the view. One is “Most Viewed”, the other “Recently on Lifehacker”…
Apologies, broken tag. Fixed now.
Apologies, broken tag. Fixed now.
So, shouldst though lie back like that on a chair to improve their posture? I think my problem is I am sticking my chest out trying to improve my posture but that just makes it even more deformed.
I’m only 22 but I’ve always tried to be careful with my posture. Since I spend so much time at home on the computer, last year I bought an adjustable $800 high back ergonomic mesh chair, one of the best in the world and I have to say that it really works wonders, no more shifting around or becoming uncomfortable.
I’m also interested in standing desks, but that is out of the question for my massive computer setup. However if I had to sit at a computer at work and I had the option I would definitely use one. That or buy another chair to use there because I won’t sacrifice my back for a pay-check.
Yes the 135 degree angle really isn’t something you could work with at the office or work place! I currently use The Bambach Saddle Seat the rationale behind this seat is that keeps your hips in an upright (neutral) position whilst seated hence, promoting the natural curvature of the spine keeping that “s” shape rather than the C shaped hunched position that most seats encourage!